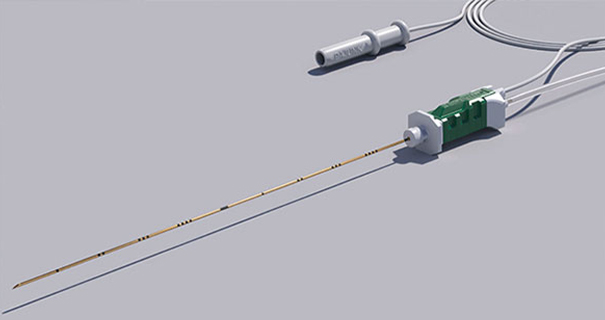
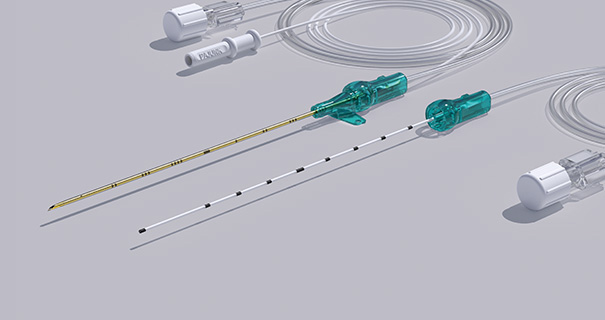
SonoLong SoftSecure

SonoLong SoftSecure
Catheter Placement for Peripheral Nerve Blocks
Clinical Requirements - Precision in Catheter Placement
Precise and permanent placement of the catheter is of crucial importance for reliable performance of peripheral nerve blocks. Marhofer et al.1 have analyzed the causes and consequences of catheter misplacement in detail. Among other things, they found a highly significant correlation between dwell time and dislocation rate of the catheter for interscalene and femoral nerves.
Primary dislocation
If the catheter is pushed further through the nerve, the anesthetic not only misses its target area, but serious complications such as injury to nerve structures and blood vessels can also occur.
Secondary dislocation
Early mobilization of patients also carries the risk of catheter migration. This can damage vessels or nerves and the effectiveness of regional anesthesia cannot be guaranteed.
Catheter misplacement using the example of an interscalene block
Relevance of the Catheter Material - Atraumatic, Flexible Catheter Tip
An important starting point for reducing the dislocation rate is the quality of the catheter tip. In 2012, Shih et al. found a direct correlation between the stiffness of the catheter material and the dislocation rate during epidural block.2
This is exactly where the PAJUNK® development started off from. The result is the SonoLong SoftSecure catheter, which is characterized by a soft catheter material and is equipped with a stylet, a stainless steel spiral, and three lateral openings.
The soft tip of the SonoLong SoftSecure catheter ensures precise placement, as the tip is deflected away from the nerve wall due to the wall's resistance.
For the same reason, the catheter is also held back by the surrounding, firmer structures of the fascia and rolls up in the immediate vicinity. Further advancement of the catheter and subsequent dislocation during patient mobilization should be avoided.
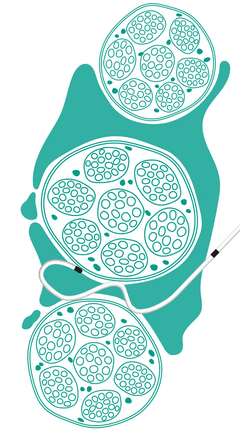
Catheter placement with SonoLong SoftSecure catheter using the example of an interscalene block
“With this combination of atraumatic, flexible catheter material and a stable architecture,
Pajunk has established a new generation of catheters that virtually eliminate dislocation.“
Frederik Lehn, Head of Development at Pajunk
SonoLong SoftSecure Set Overview
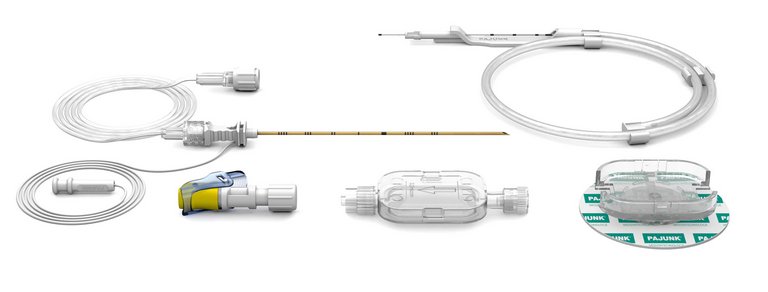
SonoLong SoftSecure Catheter Features & Advantages

Soft Catheter Material
Makes the tip soft and flexible:
- Designed to minimize the primary and secondary dislocation rates.
- Injury to nerve structures and blood vessels can be prevented from occurring.

Markings and Graduations
Outlet markings for the SonoLong needle 50 mm, 100 mm, 150 mm, and six ascending 360° markings in 5 cm increments up to 30 cm:
- Indicate where the catheter tip exits the needle.
- Support easy control of catheter position.

Catheter Container with Integrated Insertion Aid
Supports one-handed catheter insertion through the needle and tactile perception:
- Catheter placement is possible under sterile conditions since the catheter is protected by the catheter container.
- Memory effect can be avoided.

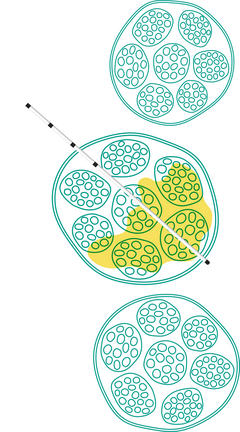
Three Lateral Openings
Arranged around the first 1.1 cm, the tip is closed:
- Optimize even distribution of the anesthetic.

Stylet Ensures Stability
Stylet is set back 5 cm from the distal end:
- Supports convenient and secure placement.
- The soft catheter tip maintains its atraumatic properties.
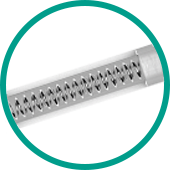
Integrated Stainless Steel Helical Coil
Ensures kink resistance and flexibility, and a stable inner lumen3.
- Enables a high anesthetic flow rate
- and a smooth connection to the injection pump.
SonoLong NanoLine® Needle Features & Advantages

Cornerstone Reflectors
360° graduations on the first 20 mm of the needle in two sections:
- Optimized ultrasound visibility of the needle shaft4.
- Reliable and optimized needle echogenicity at higher insertion angles.

NanoLine Coating
Ultra-thin polymer layer in the inner and outer lumen:
- Increased stimulation precision only through the non-insulated needle tip.
SonoLong SoftSecure Ordering Info
| Item description | Item no. LUER |
Item no.
| Purchase Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 19G x 50mm (2") with Facet Tip S / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | 531189-31A | 531169-31A | 10 |
| 19G x 100mm (4") with Facet Tip S / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | 521189-31A | 521169-31A | 10 |
| 19G x 150mm (6") with Facet Tip S / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | 511189-31A | 511169-31A | 10 |
| Item description | 19G x 50mm (2") with Facet Tip S / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | |
|---|---|---|
| Item no. LUER | 531189-31A | 10 |
| Item no. | 531169-31A | 10 |
| Item description | 19G x 100mm (4") with Facet Tip S / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | |
| Item no. LUER | 521189-31A | 10 |
| Item no. | 521169-31A | 10 |
| Item description | 19G x 150mm (6") with Facet Tip S / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | |
| Item no. LUER | 511189-31A | 10 |
| Item no. | 511169-31A | 10 |
| Item description | Item no. LUER |
Item no.
| Purchase Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18G x 50mm (2") with Tuohy Tip / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | 531189-31C | 531169-31C | 10 |
| 18G x 100mm (4") with Tuohy Tip / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | 521189-31C | 521169-31C | 10 |
| Item description | 18G x 50mm (2") with Tuohy Tip / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | |
|---|---|---|
| Item no. LUER | 531189-31C | 10 |
| Item no. | 531169-31C | 10 |
| Item description | 18G x 100mm (4") with Tuohy Tip / 20G x 50cm catheter with closed tip and 3 lateral openings / Clamping Adapter / Filter 0,2µm / FixoLong | |
| Item no. LUER | 521189-31C | 10 |
| Item no. | 521169-31C | 10 |
Incl. 2 posters for: Trauma and Thoracic Trauma. Dedicated to Emergency Doctors and other non-anaesthesia professionals who deal with trauma patients
Incl. 4 posters for: upper limb, lower limb, trunk and ankle. Dedicated to Anaesthesiologists
Studies:
1 Marhofer D. et al. (2013). Dislocation rates of perineural catheters: a volunteer study. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 111: 800–806.
2 Shih C.-K. et al. (2012). Soft catheters reduce the risk of intravascular cannulation during epidural block. Koahsiung Journal of Medical Science, 28: 373–376.
3 Toledano, R. D. et al. (2014). Epidural Catheter Design – Histroy, Innovations and Clinical Implications. Anesthesiology, V 121, No 1.
4 Fuzier R. et al. (2015). The echogenicity of nerve blockade needles. Anesth., 70: 462–466.
NRFit® is a registered trademark of GEDSA and is used with their permission
Not all products are registered and approved for sale in all countries or regions. Indications of use may also vary by country and region. Please contact your country representative for product availability and information. Product images are for reference only.